Writing a test is typically a three-step process:
The concepts used in this documentation are as follows:
The rest of this manual will explain the following:
| @BeforeSuite @AfterSuite @BeforeTest @AfterTest @BeforeGroups @AfterGroups @BeforeClass @AfterClass @BeforeMethod @AfterMethod | Configuration information for a TestNG class:
@BeforeSuite: The annotated method will be run before all tests in this suite have run. @AfterSuite: The annotated method will be run after all tests in this suite have run. @BeforeTest: The annotated method will be run before any test method belonging to the classes inside the <test> tag is run. @AfterTest: The annotated method will be run after all the test methods belonging to the classes inside the <test> tag have run. @BeforeGroups: The list of groups that this configuration method will run before. This method is guaranteed to run shortly before the first test method that belongs to any of these groups is invoked. @AfterGroups: The list of groups that this configuration method will run after. This method is guaranteed to run shortly after the last test method that belongs to any of these groups is invoked. @BeforeClass: The annotated method will be run before the first test method in the current class is invoked. @AfterClass: The annotated method will be run after all the test methods in the current class have been run. @BeforeMethod: The annotated method will be run before each test method. @AfterMethod: The annotated method will be run after each test method. |
|
| alwaysRun |
For before methods (beforeSuite, beforeTest, beforeTestClass and
beforeTestMethod, but not beforeGroups):
If set to true, this configuration method will be run
regardless of what groups it belongs to.
For after methods (afterSuite, afterClass, ...): If set to true, this configuration method will be run even if one or more methods invoked previously failed or was skipped. |
|
| dependsOnGroups | The list of groups this method depends on. | |
| dependsOnMethods | The list of methods this method depends on. | |
| enabled | Whether methods on this class/method are enabled. | |
| groups | The list of groups this class/method belongs to. | |
| inheritGroups | If true, this method will belong to groups specified in the @Test annotation at the class level. | |
| @DataProvider | Marks a method as supplying data for a test method. The annotated method must return an Object[][] where each Object[] can be assigned the parameter list of the test method. The @Test method that wants to receive data from this DataProvider needs to use a dataProvider name equals to the name of this annotation. | |
| name | The name of this data provider. If it's not supplied, the name of this data provider will automatically be set to the name of the method. | |
| parallel | If set to true, tests generated using this data provider are run in parallel. Default value is false. | |
| @Factory | Marks a method as a factory that returns objects that will be used by TestNG as Test classes. The method must return Object[]. | |
| @Listeners | Defines listeners on a test class. | |
| value | An array of classes that extend org.testng.ITestNGListener. | |
| @Parameters | Describes how to pass parameters to a @Test method. | |
| value | The list of variables used to fill the parameters of this method. | |
| @Test | Marks a class or a method as part of the test. | |
| alwaysRun | If set to true, this test method will always be run even if it depends on a method that failed. | |
| dataProvider | The name of the data provider for this test method. | |
| dataProviderClass | The class where to look for the data provider. If not specified, the data provider will be looked on the class of the current test method or one of its base classes. If this attribute is specified, the data provider method needs to be static on the specified class. | |
| dependsOnGroups | The list of groups this method depends on. | |
| dependsOnMethods | The list of methods this method depends on. | |
| description | The description for this method. | |
| enabled | Whether methods on this class/method are enabled. | |
| expectedExceptions | The list of exceptions that a test method is expected to throw. If no exception or a different than one on this list is thrown, this test will be marked a failure. | |
| groups | The list of groups this class/method belongs to. | |
| invocationCount | The number of times this method should be invoked. | |
| invocationTimeOut | The maximum number of milliseconds this test should take for the cumulated time of all the invocationcounts. This attribute will be ignored if invocationCount is not specified. | |
| priority | The priority for this test method. Lower priorities will be scheduled first. | |
| successPercentage | The percentage of success expected from this method | |
| singleThreaded | If set to true, all the methods on this test class are guaranteed to run in the same thread, even if the tests are currently being run with parallel="methods". This attribute can only be used at the class level and it will be ignored if used at the method level. Note: this attribute used to be called sequential (now deprecated). | |
| timeOut | The maximum number of milliseconds this test should take. | |
| threadPoolSize |
The size of the thread pool for this method.
The method will be invoked from multiple threads as specified by
invocationCount. Note: this attribute is ignored if invocationCount is not specified |
|
You can invoke TestNG in several different ways:
This section describes the format of testng.xml (you will find documentation on ant and the command line below).
The current DTD for testng.xml can be found on the main Web site: http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd (for your convenience, you might prefer to browse the HTML version).
Here is an example testng.xml file:
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1" verbose="1" >
<test name="Nopackage" >
<classes>
<class name="NoPackageTest" />
</classes>
</test>
<test name="Regression1">
<classes>
<class name="test.sample.ParameterSample"/>
<class name="test.sample.ParameterTest"/>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
You can specify package names instead of class names:
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Suite1" verbose="1" >
<test name="Regression1" >
<packages>
<package name="test.sample" />
</packages>
</test>
</suite>
In this example, TestNG will look at all the classes in the package test.sample and will retain only classes that have TestNG annotations.
You can also specify groups and methods to be included and excluded:
<test name="Regression1">
<groups>
<run>
<exclude name="brokenTests" />
<include name="checkinTests" />
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="test.IndividualMethodsTest">
<methods>
<include name="testMethod" />
</methods>
</class>
</classes>
</test>
You can also define new groups inside testng.xml and specify additional details in attributes, such as whether to run the tests in parallel, how many threads to use, whether you are running JUnit tests, etc...
By default, TestNG will run your tests in the order they are found in the XML file. If you want the classes and methods listed in this file to be run in an unpredictible order, set the preserve-order attribute to false
<test name="Regression1" preserve-order="false">
<classes>
<class name="test.Test1">
<methods>
<include name="m1" />
<include name="m2" />
</methods>
</class>
<class name="test.Test2" />
</classes>
</test>
Please see the DTD for a complete list of the features, or read on.
Assuming that you have TestNG in your class path, the simplest way to invoke TestNG is as follows:
java org.testng.TestNG testng1.xml [testng2.xml testng3.xml ...]You need to specify at least one XML file describing the TestNG suite you are trying to run. Additionally, the following command-line switches are available:
| Option | Argument | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| -configfailurepolicy | skip|continue | Whether TestNG should continue to execute the remaining tests in the suite or skip them if an @Before* method fails. Default behavior is skip. |
| -d | A directory | The directory where the reports will be generated (defaults to test-output). |
| -dataproviderthreadcount | The default number of threads to use for data providers when running tests in parallel. | This sets the default maximum number of threads to use for data providers when running tests in parallel. It will only take effect if the parallel mode has been selected (for example, with the -parallel option). This can be overridden in the suite definition. |
| -excludegroups | A comma-separated list of groups. | The list of groups you want to be excluded from this run. |
| -groups | A comma-separated list of groups. | The list of groups you want to run (e.g. "windows,linux,regression"). |
| -listener | A comma-separated list of Java classes that can be found on your classpath. | Lets you specify your own test listeners. The classes need to implement org.testng.ITestListener |
| -methods | A comma separated list of fully qualified class name and method. For example com.example.Foo.f1,com.example.Bar.f2. | Lets you specify individual methods to run. |
| -methodselectors | A comma-separated list of Java classes and method priorities that define method selectors. | Lets you specify method selectors on the command line. For example: com.example.Selector1:3,com.example.Selector2:2 |
| -parallel | methods|tests|classes | If specified, sets the default mechanism used to determine how to use parallel threads when running tests. If not set, default mechanism is not to use parallel threads at all. This can be overridden in the suite definition. |
| -reporter | The extended configuration for a custom report listener. | Similar to the -listener option, except that it allows the configuration of JavaBeans-style properties on the reporter instance.
Example: -reporter com.test.MyReporter:methodFilter=*insert*,enableFiltering=true You can have as many occurences of this option, one for each reporter that needs to be added. |
| -sourcedir | A semi-colon separated list of directories. | The directories where your javadoc annotated test sources are. This option is only necessary if you are using javadoc type annotations. (e.g. "src/test" or "src/test/org/testng/eclipse-plugin;src/test/org/testng/testng"). |
| -suitename | The default name to use for a test suite. | This specifies the suite name for a test suite defined on the command line. This option is ignored if the suite.xml file or the source code specifies a different suite name. It is possible to create a suite name with spaces in it if you surround it with double-quotes "like this". |
| -testclass | A comma-separated list of classes that can be found in your classpath. | A list of class files separated by commas (e.g. "org.foo.Test1,org.foo.test2"). |
| -testjar | A jar file. | Specifies a jar file that contains test classes. If a testng.xml file is found at the root of that jar file, it will be used, otherwise, all the test classes found in this jar file will be considered test classes. |
| -testname | The default name to use for a test. | This specifies the name for a test defined on the command line. This option is ignored if the suite.xml file or the source code specifies a different test name. It is possible to create a test name with spaces in it if you surround it with double-quotes "like this". |
| -testnames | A comma separated list of test names. | Only tests defined in a <test> tag matching one of these names will be run. |
| -testrunfactory | A Java classes that can be found on your classpath. | Lets you specify your own test runners. The class needs to implement org.testng.ITestRunnerFactory. |
| -threadcount | The default number of threads to use when running tests in parallel. | This sets the default maximum number of threads to use for running tests in parallel. It will only take effect if the parallel mode has been selected (for example, with the -parallel option). This can be overridden in the suite definition. |
| -xmlpathinjar | The path of the XML file inside the jar file. | This attribute should contain the path to a valid XML file inside the test jar (e.g. "resources/testng.xml"). The default is "testng.xml", which means a file called "testng.xml" at the root of the jar file. This option will be ignored unless -testjar is specified. |
This documentation can be obtained by invoking TestNG without any arguments.
You can also put the command line switches in a text file, say c:\command.txt, and tell TestNG to use that file to retrieve its parameters:
C:> more c:\command.txt -d test-output testng.xml C:> java org.testng.TestNG @c:\command.txt
Additionally, TestNG can be passed properties on the command line of the Java Virtual Machine, for example
java -Dtestng.test.classpath="c:/build;c:/java/classes;" org.testng.TestNG testng.xmlHere are the properties that TestNG understands:
| Property | Type | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| testng.test.classpath | A semi-colon separated series of directories that contain your test classes. | If this property is set, TestNG will use it to look for your test classes instead of the class path. This is convenient if you are using the package tag in your XML file and you have a lot of classes in your classpath, most of them not being test classes. |
java org.testng.TestNG -groups windows,linux -testclass org.test.MyTestThe ant task and testng.xml allow you to launch TestNG with more parameters (methods to include, specifying parameters, etc...), so you should consider using the command line only when you are trying to learn about TestNG and you want to get up and running quickly.
Important: The command line flags that specify what tests should be run will be ignored if you also specify a testng.xml file, with the exception of -includedgroups and -excludedgroups, which will override all the group inclusions/exclusions found in testng.xml.
<suite allow-return-values="true"> or <test allow-return-values="true">
TestNG allows you to perform sophisticated groupings of test methods. Not only can you declare that methods belong to groups, but you can also specify groups that contain other groups. Then TestNG can be invoked and asked to include a certain set of groups (or regular expressions) while excluding another set. This gives you maximum flexibility in how you partition your tests and doesn't require you to recompile anything if you want to run two different sets of tests back to back.
Groups are specified in your testng.xml file and can be found either under the <test> or <suite> tag. Groups specified in the <suite> tag apply to all the <test> tags underneath. Note that groups are accumulative in these tags: if you specify group "a" in <suite> and "b" in <test>, then both "a" and "b" will be included.
For example, it is quite common to have at least two categories of tests
public class Test1 {
@Test(groups = { "functest", "checkintest" })
public void testMethod1() {
}
@Test(groups = {"functest", "checkintest"} )
public void testMethod2() {
}
@Test(groups = { "functest" })
public void testMethod3() {
}
}
Invoking TestNG with
<test name="Test1">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="functest"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="example1.Test1"/>
</classes>
</test>
will run all the test methods in that classes, while invoking it with checkintest will only run testMethod1() and testMethod2().
Here is another example, using regular expressions this time. Assume that some of your test methods should not be run on Linux, your test would look like:
@Test
public class Test1 {
@Test(groups = { "windows.checkintest" })
public void testWindowsOnly() {
}
@Test(groups = {"linux.checkintest"} )
public void testLinuxOnly() {
}
@Test(groups = { "windows.functest" )
public void testWindowsToo() {
}
}
You could use the following testng.xml to launch only the Windows methods:
<test name="Test1">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="windows.*"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="example1.Test1"/>
</classes>
</test>
Note: TestNG uses regular expressions, and not wildmats. Be aware of the difference (for example, "anything" is matched by ".*" -- dot star -- and not "*").
<test name="Test1">
<classes>
<class name="example1.Test1">
<methods>
<include name=".*enabledTestMethod.*"/>
<exclude name=".*brokenTestMethod.*"/>
</methods>
</class>
</classes>
</test>
This can come in handy to deactivate a single method without having to recompile
anything, but I don't recommend using this technique too much since it makes
your testing framework likely to break if you start refactoring your Java code
(the regular expressions used in the tags might not match your methods any
more).
<test name="Regression1">
<groups>
<define name="functest">
<include name="windows"/>
<include name="linux"/>
</define>
<define name="all">
<include name="functest"/>
<include name="checkintest"/>
</define>
<run>
<include name="all"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="test.sample.Test1"/>
</classes>
</test>
TestNG allows you to include groups as well as exclude them.
For example, it is quite usual to have tests that temporarily break because of a recent change, and you don't have time to fix the breakage yet. 4 However, you do want to have clean runs of your functional tests, so you need to deactivate these tests but keep in mind they will need to be reactivated.A simple way to solve this problem is to create a group called "broken" and make these test methods belong to it. For example, in the above example, I know that testMethod2() is now broken so I want to disable it:
@Test(groups = {"checkintest", "broken"} )
public void testMethod2() {
}
All I need to do now is to exclude this group from the run:
<test name="Simple example">
<groups>
<run>
<include name="checkintest"/>
<exclude name="broken"/>
</run>
</groups>
<classes>
<class name="example1.Test1"/>
</classes>
</test>
This way, I will get a clean test run while keeping track of what tests are broken and need to be fixed later.
Note: you can also disable tests on an individual basis by using the "enabled" property available on both @Test and @Before/After annotations.
@Test(groups = { "checkin-test" })
public class All {
@Test(groups = { "func-test" )
public void method1() { ... }
public void method2() { ... }
}
In this class, method2() is part of the group "checkin-test", which is defined
at the class level, while method1() belongs to both "checkin-test" and
"func-test".
Test methods don't have to be parameterless. You can use an arbitrary number of parameters on each of your test method, and you instruct TestNG to pass you the correct parameters with the @Parameters annotation.
There are two ways to set these parameters: with testng.xml or programmatically.
@Parameters({ "first-name" })
@Test
public void testSingleString(String firstName) {
System.out.println("Invoked testString " + firstName);
assert "Cedric".equals(firstName);
}
In this code, we specify that the parameter firstName of your Java method
should receive the value of the XML parameter called first-name.
This XML parameter is defined in testng.xml:
<suite name="My suite"> <parameter name="first-name" value="Cedric"/> <test name="Simple example"> <-- ... -->
@Parameters({ "datasource", "jdbcDriver" })
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeTest(String ds, String driver) {
m_dataSource = ...; // look up the value of datasource
m_jdbcDriver = driver;
}
This time, the two Java parameter ds
and driver will receive the value given to the properties datasource
and jdbc-driver respectively.
Parameters can be declared optional with the Optional annotation:
@Parameters("db")
@Test
public void testNonExistentParameter(@Optional("mysql") String db) { ... }
If no parameter named "db" is found in your testng.xml file, your test method will receive the default value specified inside the @Optional annotation: "mysql".
The @Parameters annotation can be placed at the following locations:
Notes:
- The XML parameters are mapped to the Java parameters in the same order as they are found in the annotation, and TestNG will issue an error if the numbers don't match.
- Parameters are scoped. In testng.xml, you can declare them either under a <suite> tag or under <test>. If two parameters have the same name, it's the one defined in <test> that has precedence. This is convenient if you need to specify a parameter applicable to all your tests and override its value only for certain tests.
Specifying parameters in testng.xml might not be sufficient if you need to pass complex parameters, or parameters that need to be created from Java (complex objects, objects read from a property file or a database, etc...). In this case, you can use a Data Provider to supply the values you need to test. A Data Provider is a method on your class that returns an array of array of objects. This method is annotated with @DataProvider:
//This method will provide data to any test method that declares that its Data Provider
//is named "test1"
@DataProvider(name = "test1")
public Object[][] createData1() {
return new Object[][] {
{ "Cedric", new Integer(36) },
{ "Anne", new Integer(37)},
};
}
//This test method declares that its data should be supplied by the Data Provider
//named "test1"
@Test(dataProvider = "test1")
public void verifyData1(String n1, Integer n2) {
System.out.println(n1 + " " + n2);
}
will print
Cedric 36 Anne 37A @Test method specifies its Data Provider with the dataProvider attribute. This name must correspond to a method on the same class annotated with @DataProvider(name="...") with a matching name.
By default, the data provider will be looked for in the current test class or one of its base classes. If you want to put your data provider in a different class, it needs to be a static method or a class with a non-arg constructor, and you specify the class where it can be found in the dataProviderClass attribute:
public class StaticProvider {
@DataProvider(name = "create")
public static Object[][] createData() {
return new Object[][] {
new Object[] { new Integer(42) }
};
}
}
public class MyTest {
@Test(dataProvider = "create", dataProviderClass = StaticProvider.class)
public void test(Integer n) {
// ...
}
}
The data provider supports injection too. TestNG will use the test context for the injection.
The Data Provider method can return one of the following two types:
@DataProvider(name = "test1")
public Iterator<Object[]> createData() {
return new MyIterator(DATA);
}
If you declare your @DataProvider as taking a java.lang.reflect.Method
as first parameter, TestNG will pass the current test method for this
first parameter. This is particularly useful when several test methods
use the same @DataProvider and you want it to return different
values depending on which test method it is supplying data for.
For example, the following code prints the name of the test method inside its @DataProvider:
@DataProvider(name = "dp")
public Object[][] createData(Method m) {
System.out.println(m.getName()); // print test method name
return new Object[][] { new Object[] { "Cedric" }};
}
@Test(dataProvider = "dp")
public void test1(String s) {
}
@Test(dataProvider = "dp")
public void test2(String s) {
}
and will therefore display:
test1 test2Data providers can run in parallel with the attribute parallel:
@DataProvider(parallel = true) // ...Parallel data providers running from an XML file share the same pool of threads, which has a size of 10 by default. You can modify this value in the <suite> tag of your XML file:
<suite name="Suite1" data-provider-thread-count="20" > ...If you want to run a few specific data providers in a different thread pool, you need to run them from a different XML file.
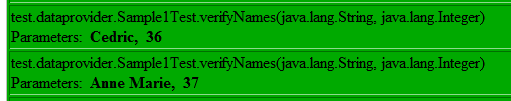
Parameters used to invoke your test methods are shown in the HTML reports generated by TestNG. Here is an example:

Sometimes, you need your test methods to be invoked in a certain order. Here are a few examples:
You can use the attributes dependsOnMethods or dependsOnGroups, found on the @Test annotation.
There are two kinds of dependencies:
@Test
public void serverStartedOk() {}
@Test(dependsOnMethods = { "serverStartedOk" })
public void method1() {}
In this example, method1() is declared as depending on method serverStartedOk(), which guarantees that serverStartedOk() will always be invoked first.
You can also have methods that depend on entire groups:
@Test(groups = { "init" })
public void serverStartedOk() {}
@Test(groups = { "init" })
public void initEnvironment() {}
@Test(dependsOnGroups = { "init.*" })
public void method1() {}
In this example, method1() is declared as depending on any group matching the regular expression "init.*", which guarantees that the methods serverStartedOk() and initEnvironment() will always be invoked before method1().
Note: as stated before, the order of invocation for methods that belong in the same group is not guaranteed to be the same across test runs.
If a method depended upon fails and you have a hard dependency on it (alwaysRun=false, which is the default), the methods that depend on it are not marked as FAIL but as SKIP. Skipped methods will be reported as such in the final report (in a color that is neither red nor green in HTML), which is important since skipped methods are not necessarily failures.
Both dependsOnGroups and dependsOnMethods accept regular expressions as parameters. For dependsOnMethods, if you are depending on a method which happens to have several overloaded versions, all the overloaded methods will be invoked. If you only want to invoke one of the overloaded methods, you should use dependsOnGroups.
For a more advanced example of dependent methods, please refer to this article, which uses inheritance to provide an elegant solution to the problem of multiple dependencies.
By default, dependent methods are grouped by class. For example, if method b() depends on method a() and you have several instances of the class that contains these methods (because of a factory of a data provider), then the invocation order will be as follows:a(1) a(2) b(2) b(2)TestNG will not run b() until all the instances have invoked their a() method.
This behavior might not be desirable in certain scenarios, such as for example testing a sign in and sign out of a web browser for various countries. In such a case, you would like the following ordering:
signIn("us")
signOut("us")
signIn("uk")
signOut("uk")
For this ordering, you can use the XML attribute group-by-instances. This attribute is valid either on <suite> or <test>:
<suite name="Factory" group-by-instances="true"> or <test name="Factory" group-by-instances="true">
<test name="My suite">
<groups>
<dependencies>
<group name="c" depends-on="a b" />
<group name="z" depends-on="c" />
</dependencies>
</groups>
</test>
The <depends-on> attribute contains a space-separated list of groups.
public class TestWebServer {
@Test(parameters = { "number-of-times" })
public void accessPage(int numberOfTimes) {
while (numberOfTimes-- > 0) {
// access the web page
}
}
}
<test name="T1"> <parameter name="number-of-times" value="10"/> <class name= "TestWebServer" /> </test> <test name="T2"> <parameter name="number-of-times" value="20"/> <class name= "TestWebServer"/> </test> <test name="T3"> <parameter name="number-of-times" value="30"/> <class name= "TestWebServer"/> </test>This can become quickly impossible to manage, so instead, you should use a factory:
public class WebTestFactory {
@Factory
public Object[] createInstances() {
Object[] result = new Object[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
result[i] = new WebTest(i * 10);
}
return result;
}
}
and the new test class is now:
public class WebTest {
private int m_numberOfTimes;
public WebTest(int numberOfTimes) {
m_numberOfTimes = numberOfTimes;
}
@Test
public void testServer() {
for (int i = 0; i < m_numberOfTimes; i++) {
// access the web page
}
}
}
Your testng.xml only needs to reference the class that contains the factory method, since the test instances themselves will be created at runtime:
<class name="WebTestFactory" />
The factory method can receive parameters just like @Test and @Before/After and it must return Object[]. The objects returned can be of any class (not necessarily the same class as the factory class) and they don't even need to contain TestNG annotations (in which case they will be ignored by TestNG).
Factories can also be used with data providers, and you can leverage this functionality by putting the @Factory annotation either on a regular method or on a constructor. Here is an example of a constructor factory:
@Factory(dataProvider = "dp")
public FactoryDataProviderSampleTest(int n) {
super(n);
}
@DataProvider
static public Object[][] dp() {
return new Object[][] {
new Object[] { 41 },
new Object[] { 42 },
};
}
The example will make TestNG create two test classes, on with the constructor invoked with the value 41 and the other with 42.
@Test
public class Test1 {
public void test1() {
}
public void test2() {
}
}
The effect of a class level @Test annotation is to make all the public methods of this class to become test methods even if they are not annotated. You can still repeat the @Test annotation on a method if you want to add certain attributes.
For example:
@Test
public class Test1 {
public void test1() {
}
@Test(groups = "g1")
public void test2() {
}
}
will make both test1() and test2() test methods but on top of that, test2() now belongs to the group "g1".
java org.testng.TestNG -suitethreadpoolsize 3 testng1.xml testng2.xml testng3.xmlThe corresponding ant task name is suitethreadpoolsize.
<suite name="My suite" parallel="methods" thread-count="5">
<suite name="My suite" parallel="tests" thread-count="5">
<suite name="My suite" parallel="classes" thread-count="5">
<suite name="My suite" parallel="instances" thread-count="5">
Additionally, the attribute thread-count allows you to specify how many threads should be allocated for this execution.
You can also specify that a @Test method should be invoked from different threads. You can use the attribute threadPoolSize to achieve this result:Note: the @Test attribute timeOut works in both parallel and non-parallel mode.
@Test(threadPoolSize = 3, invocationCount = 10, timeOut = 10000)
public void testServer() {
In this example, the function testServer will be invoked ten times from three different threads. Additionally, a time-out of ten seconds guarantees that none of the threads will block on this thread forever.
java -classpath testng.jar;%CLASSPATH% org.testng.TestNG -d test-outputs testng.xml java -classpath testng.jar;%CLASSPATH% org.testng.TestNG -d test-outputs test-outputs\testng-failed.xml
Note that testng-failed.xml will contain all the necessary dependent methods so that you are guaranteed to run the methods that failed without any SKIP failures.
<test name="Test1" junit="true">
<classes>
<!-- ... -->
The behavior of TestNG in this case is similar to JUnit depending on the JUnit version found on the class path:
TestListenerAdapter tla = new TestListenerAdapter();
TestNG testng = new TestNG();
testng.setTestClasses(new Class[] { Run2.class });
testng.addListener(tla);
testng.run();
This example creates a TestNG object and runs the test class Run2. It also adds a TestListener. You can either use the adapter class org.testng.TestListenerAdapter or implement org.testng.ITestListener yourself. This interface contains various callback methods that let you keep track of when a test starts, succeeds, fails, etc...
Similary, you can invoke TestNG on a testng.xml file or you can create a virtual testng.xml file yourself. In order to do this, you can use the classes found the package org.testng.xml: XmlClass, XmlTest, etc... Each of these classes correspond to their XML tag counterpart.
For example, suppose you want to create the following virtual file:
<suite name="TmpSuite" >
<test name="TmpTest" >
<classes>
<class name="test.failures.Child" />
<classes>
</test>
</suite>
You would use the following code:
XmlSuite suite = new XmlSuite();
suite.setName("TmpSuite");
XmlTest test = new XmlTest(suite);
test.setName("TmpTest");
List<XmlClass> classes = new ArrayList<XmlClass>();
classes.add(new XmlClass("test.failures.Child"));
test.setXmlClasses(classes) ;
And then you can pass this XmlSuite to TestNG:
List<XmlSuite> suites = new ArrayList<XmlSuite>(); suites.add(suite); TestNG tng = new TestNG(); tng.setXmlSuites(suites); tng.run();
Please see the JavaDocs for the entire API.
If the <include> and <exclude> tags in testng.xml are not enough for your needs, you can use a BeanShell expression to decide whether a certain test method should be included in a test run or not. You specify this expression just under the <test> tag:
<test name="BeanShell test">
<method-selectors>
<method-selector>
<script language="beanshell"><![CDATA[
groups.containsKey("test1")
]]></script>
</method-selector>
</method-selectors>
<!-- ... -->
When a <script> tag is found in testng.xml, TestNG will ignore subsequent <include> and <exclude> of groups and methods in the current <test> tag: your BeanShell expression will be the only way to decide whether a test method is included or not.Here are additional information on the BeanShell script:
In order to achieve this, you need to use an Annotation Transformer.
An Annotation Transformer is a class that implements the following interface:
public interface IAnnotationTransformer {
/**
* This method will be invoked by TestNG to give you a chance
* to modify a TestNG annotation read from your test classes.
* You can change the values you need by calling any of the
* setters on the ITest interface.
*
* Note that only one of the three parameters testClass,
* testConstructor and testMethod will be non-null.
*
* @param annotation The annotation that was read from your
* test class.
* @param testClass If the annotation was found on a class, this
* parameter represents this class (null otherwise).
* @param testConstructor If the annotation was found on a constructor,
* this parameter represents this constructor (null otherwise).
* @param testMethod If the annotation was found on a method,
* this parameter represents this method (null otherwise).
*/
public void transform(ITest annotation, Class testClass,
Constructor testConstructor, Method testMethod);
}
Like all the other TestNG listeners, you can specify this class either on the command line or with ant:
java org.testng.TestNG -listener MyTransformer testng.xmlor programmatically:
TestNG tng = new TestNG(); tng.setAnnotationTransformer(new MyTransformer()); // ...When the method transform() is invoked, you can call any of the setters on the ITest test parameter to alter its value before TestNG proceeds further.
For example, here is how you would override the attribute invocationCount but only on the test method invoke() of one of your test classes:
public class MyTransformer implements IAnnotationTransformer {
public void transform(ITest annotation, Class testClass,
Constructor testConstructor, Method testMethod)
{
if ("invoke".equals(testMethod.getName())) {
annotation.setInvocationCount(5);
}
}
}
IAnnotationTransformer only lets you modify a @Test annotation. If you need to modify another TestNG annotation (a configuration annotation, @Factory or @DataProvider), use an IAnnotationTransformer2.
public interface IMethodInterceptor {
List<IMethodInstance> intercept(List<IMethodInstance> methods, ITestContext context);
}
The list of methods passed in parameters are all the methods that can be run in any order. Your intercept method is expected to return a similar list of IMethodInstance, which can be either of the following:
java -classpath "testng-jdk15.jar:test/build" org.testng.TestNG -listener test.methodinterceptors.NullMethodInterceptor -testclass test.methodinterceptors.FooTestFor the equivalent ant syntax, see the listeners attribute in the ant documentation.
For example, here is a Method Interceptor that will reorder the methods so that test methods that belong to the group "fast" are always run first:
public List<IMethodInstance> intercept(List<IMethodInstance> methods, ITestContext context) {
List<IMethodInstance> result = new ArrayList<IMethodInstance>();
for (IMethodInstance m : methods) {
Test test = m.getMethod().getConstructorOrMethod().getAnnotation(Test.class);
Set<String> groups = new HashSet<String>();
for (String group : test.groups()) {
groups.add(group);
}
if (groups.contains("fast")) {
result.add(0, m);
}
else {
result.add(m);
}
}
return result;
}
<suite>
<listeners>
<listener class-name="com.example.MyListener" />
<listener class-name="com.example.MyMethodInterceptor" />
</listeners>
...
Or if you prefer to define these listeners in Java:
@Listeners({ com.example.MyListener.class, com.example.MyMethodInterceptor.class })
public class MyTest {
// ...
}
The @Listeners annotation can contain any class that extends org.testng.ITestNGListener except IAnnotationTransformer and IAnnotationTransformer2. The reason is that these listeners need to be known very early in the process so that TestNG can use them to rewrite your annotations, therefore you need to specify these listeners in your testng.xml file.
Note that the @Listeners annotation will apply to your entire suite file, just as if you had specified it in a testng.xml file. If you want to restrict its scope (for example, only running on the current class), the code in your listener could first check the test method that's about to run and decide what to do then.
With ServiceLoader, all you need to do is create a jar file that contains your listener(s) and a few configuration files, put that jar file on the classpath when you run TestNG and TestNG will automatically find them.
Here is a concrete example of how it works.
Let's start by creating a listener (any TestNG listener should work):
package test.tmp;
public class TmpSuiteListener implements ISuiteListener {
@Override
public void onFinish(ISuite suite) {
System.out.println("Finishing");
}
@Override
public void onStart(ISuite suite) {
System.out.println("Starting");
}
}
Compile this file, then create a file at the location META-INF/services/org.testng.ITestNGListener, which will name the implementation(s) you want for this interface.
You should end up with the following directory structure, with only two files:
$ tree |____META-INF | |____services | | |____org.testng.ITestNGListener |____test | |____tmp | | |____TmpSuiteListener.class $ cat META-INF/services/org.testng.ITestNGListener test.tmp.TmpSuiteListenerCreate a jar of this directory:
$ jar cvf ../sl.jar . added manifest ignoring entry META-INF/ adding: META-INF/services/(in = 0) (out= 0)(stored 0%) adding: META-INF/services/org.testng.ITestNGListener(in = 26) (out= 28)(deflated -7%) adding: test/(in = 0) (out= 0)(stored 0%) adding: test/tmp/(in = 0) (out= 0)(stored 0%) adding: test/tmp/TmpSuiteListener.class(in = 849) (out= 470)(deflated 44%)Next, put this jar file on your classpath when you invoke TestNG:
$ java -classpath sl.jar:testng.jar org.testng.TestNG testng-single.yaml
Starting
f2 11 2
PASSED: f2("2")
Finishing
This mechanism allows you to apply the same set of listeners to an entire organization just by adding a jar file to the classpath, instead of asking every single developer to remember to specify these listeners in their testng.xml file.
public class NoInjectionTest {
@DataProvider(name = "provider")
public Object[][] provide() throws Exception {
return new Object[][] { { CC.class.getMethod("f") } };
}
@Test(dataProvider = "provider")
public void withoutInjection(@NoInjection Method m) {
Assert.assertEquals(m.getName(), "f");
}
@Test(dataProvider = "provider")
public void withInjection(Method m) {
Assert.assertEquals(m.getName(), "withInjection");
}
}
@Guice(modules = GuiceExampleModule.class)
public class GuiceTest extends SimpleBaseTest {
@Inject
ISingleton m_singleton;
@Test
public void singletonShouldWork() {
m_singleton.doSomething();
}
}
In this example, GuiceExampleModule is expected to bind the interface ISingleton to some concrete class:
public class GuiceExampleModule implements Module {
@Override
public void configure(Binder binder) {
binder.bind(ISingleton.class).to(ExampleSingleton.class).in(Singleton.class);
}
}
If you need more flexibility in specifying which modules should be used to instantiate your test classes, you can specify a module factory:
@Guice(moduleFactory = ModuleFactory.class)
public class GuiceModuleFactoryTest {
@Inject
ISingleton m_singleton;
@Test
public void singletonShouldWork() {
m_singleton.doSomething();
}
}
The module factory needs to implement the interface IModuleFactory:
public interface IModuleFactory {
/**
* @param context The current test context
* @param testClass The test class
*
* @return The Guice module that should be used to get an instance of this
* test class.
*/
Module createModule(ITestContext context, Class<?> testClass);
}
Your factory will be passed an instance of the test context and the test class that TestNG needs to instantiate. Your createModule method should return a Guice Module that will know how to instantiate this test class. You can use the test context to find out more information about your environment, such as parameters specified in testng.xml, etc...
You will get even more flexibility and Guice power with parent-module and guice-stage suite parameters.
guice-stage allow you to chose the Stage used to create the parent injector.
The default one is DEVELOPMENT. Other allowed values are PRODUCTION and TOOL.
Here is how you can define parent-module in your test.xml file:
TestNG will create this module only once for given suite. Will also use this module for obtaining instances of test specific Guice modules and module factories, then will create child injector for each test class. With such approach you can declare all common bindings in parent-module also you can inject binding declared in parent-module in module and module factory. Here is an example of this functionality:
package com.example;
public class ParentModule extends AbstractModule {
@Override
protected void conigure() {
bind(MyService.class).toProvider(MyServiceProvider.class);
bind(MyContext.class).to(MyContextImpl.class).in(Singleton.class);
}
}
package com.example;
public class TestModule extends AbstractModule {
private final MyContext myContext;
@Inject
TestModule(MyContext myContext) {
this.myContext = myContext
}
@Override
protected void configure() {
bind(MySession.class).toInstance(myContext.getSession());
}
}
package com.example;
@Test
@Guice(modules = TestModule.class)
public class TestClass {
@Inject
MyService myService;
@Inject
MySession mySession;
public void testServiceWithSession() {
myService.serve(mySession);
}
}
As you see ParentModule declares binding for MyService and MyContext classes. Then MyContext is injected using constructor injection into TestModule class, which also declare binding for MySession. Then parent-module in test XML file is set to ParentModule class, this enables injection in TestModule. Later in TestClass you see two injections:
* MyService - binding taken from ParentModule
* MySession - binding taken from TestModule
This configuration ensures you that all tests in this suite will be run with same session instance, the MyContextImpl object is only created once per suite, this give you possibility to configure common environment state for all tests in suite.
public interface IInvokedMethodListener extends ITestNGListener {
void beforeInvocation(IInvokedMethod method, ITestResult testResult);
void afterInvocation(IInvokedMethod method, ITestResult testResult);
}
and declare it as a listener, as explained in the section about TestNG listeners.
Here is an example with JAAS:
public class MyHook implements IHookable {
public void run(final IHookCallBack icb, ITestResult testResult) {
// Preferably initialized in a @Configuration method
mySubject = authenticateWithJAAs();
Subject.doAs(mySubject, new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Object run() {
icb.callback(testResult);
}
};
}
}
A classic example for this would be to try and leverage your existing suite file and try using it for simulating a load test on your "Application under test". At the minimum you would end up duplicating the contents of your <test> tag multiple times and create a new suite xml file and work with. But this doesn't seem to scale a lot.
TestNG allows you to alter a suite (or) a test tag in your suite xml file at runtime via listeners. You achieve this by providing a listener that implements IAlterSuiteListener. Please refer to Listeners section to learn about listeners.
Here is an example that shows how the suite name is getting altered in runtime:
public class AlterSuiteNameListener implements IAlterSuiteListener {
@Override
public void alter(List<XmlSuite> suites) {
XmlSuite suite = suites.get(0);
suite.setName(getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
This listener can only be added with either of the following ways:
A test is considered successful if it completed without throwing any exception or if it threw an exception that was expected (see the documentation for the expectedExceptions attribute found on the @Test annotation).
Your test methods will typically be made of calls that can throw an exception, or of various assertions (using the Java "assert" keyword). An "assert" failing will trigger an AssertionErrorException, which in turn will mark the method as failed (remember to use -ea on the JVM if you are not seeing the assertion errors).
Here is an example test method:
@Test
public void verifyLastName() {
assert "Beust".equals(m_lastName) : "Expected name Beust, for" + m_lastName;
}
TestNG also include JUnit's Assert class, which lets you perform
assertions on complex objects:
import static org.testng.AssertJUnit.*;
//...
@Test
public void verify() {
assertEquals("Beust", m_lastName);
}
Note that the above code use a static import in order to be able to use the assertEquals method without having to prefix it by its class.
It's very easy to generate your own reports with TestNG with Listeners and Reporters:
public class DotTestListener extends TestListenerAdapter {
private int m_count = 0;
@Override
public void onTestFailure(ITestResult tr) {
log("F");
}
@Override
public void onTestSkipped(ITestResult tr) {
log("S");
}
@Override
public void onTestSuccess(ITestResult tr) {
log(".");
}
private void log(String string) {
System.out.print(string);
if (++m_count % 40 == 0) {
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
In this example, I chose to extend TestListenerAdapter, which implements ITestListener with empty methods, so I don't have to override other methods from the interface that I have no interest in. You can implement the interface directly if you prefer.
Here is how I invoke TestNG to use this new listener:
java -classpath testng.jar;%CLASSPATH% org.testng.TestNG -listener org.testng.reporters.DotTestListener test\testng.xmland the output:
........................................ ........................................ ........................................ ........................................ ........................................ ......................... =============================================== TestNG JDK 1.5 Total tests run: 226, Failures: 0, Skips: 0 ===============================================Note that when you use -listener, TestNG will automatically determine the type of listener you want to use.
public void generateReport(List<ISuite> suites, String outputDirectory)This method will be invoked by TestNG when all the suites have been run and you can inspect its parameters to access all the information on the run that was just completed.
TestNG contains a listener that takes the TestNG results and outputs an XML file that can then be fed to JUnitReport. Here is an example, and the ant task to create this report:
<target name="reports">
<junitreport todir="test-report">
<fileset dir="test-output">
<include name="*/*.xml"/>
</fileset>
<report format="noframes" todir="test-report"/>
</junitreport>
</target>
Note: a current incompatibility between the JDK 1.5 and JUnitReports prevents the frame version from working, so you need to specify "noframes" to get this to work for now.
If you need to log messages that should appear in the generated HTML reports, you can use the class org.testng.Reporter:
Reporter.log("M3 WAS CALLED");


TestNG offers an XML reporter capturing TestNG specific information that is not available in JUnit reports. This is particulary useful when the user's test environment needs to consume XML results with TestNG-specific data that the JUnit format can't provide. Below is a sample of the output of such a reporter:
<testng-results>
<suite name="Suite1">
<groups>
<group name="group1">
<method signature="com.test.TestOne.test2()" name="test2" class="com.test.TestOne"/>
<method signature="com.test.TestOne.test1()" name="test1" class="com.test.TestOne"/>
</group>
<group name="group2">
<method signature="com.test.TestOne.test2()" name="test2" class="com.test.TestOne"/>
</group>
</groups>
<test name="test1">
<class name="com.test.TestOne">
<test-method status="FAIL" signature="test1()" name="test1" duration-ms="0"
started-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z" description="someDescription2"
finished-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z">
<exception class="java.lang.AssertionError">
<short-stacktrace>
<![CDATA[
java.lang.AssertionError
... Removed 22 stack frames
]]>
</short-stacktrace>
</exception>
</test-method>
<test-method status="PASS" signature="test2()" name="test2" duration-ms="0"
started-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z" description="someDescription1"
finished-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z">
</test-method>
<test-method status="PASS" signature="setUp()" name="setUp" is-config="true" duration-ms="15"
started-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z" finished-at="2007-05-28T12:14:37Z">
</test-method>
</class>
</test>
</suite>
</testng-results>
This reporter is injected along with the other default listeners so you can get this type of output by default. The listener provides some properties that can tweak the reporter to fit your needs. The following table contains a list of these properties with a short explanation:
| Property | Comment | Default value |
|---|---|---|
| outputDirectory | A String indicating the directory where should the XML files be outputed. | The TestNG output directory |
| timestampFormat | Specifies the format of date fields that are generated by this reporter | yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss'Z' |
| fileFragmentationLevel | An integer having the values 1, 2 or 3, indicating the way that the XML files are generated:
1 - will generate all the results in one file. 2 - each suite is generated in a separate XML file that is linked to the main file. 3 - same as 2 plus separate files for test-cases that are referenced from the suite files. |
1 |
| splitClassAndPackageNames | This boolean specifies the way that class names are generated for the <class> element. For example, you will get <class class="com.test.MyTest"> for false and <class class="MyTest" package="com.test"> for true. | false |
| generateGroupsAttribute | A boolean indicating if a groups attribute should be generated for the <test-method> element. This feature aims at providing a straight-forward method of retrieving the groups that include a test method without having to surf through the <group> elements. | false |
| generateTestResultAttributes | A boolean indicating if an <attributes> tag should be generated for each <test-method> element, containing the test result attributes (See ITestResult.setAttribute() about setting test result attributes). Each attribute toString() representation will be written in a <attribute name="[attribute name]"> tag. | false |
| stackTraceOutputMethod | Specifies the type of stack trace that is to be generated for exceptions and has the following values:
0 - no stacktrace (just Exception class and message). 1 - a short version of the stack trace keeping just a few lines from the top 2 - the complete stacktrace with all the inner exceptions 3 - both short and long stacktrace |
2 |
| generateDependsOnMethods | Use this attribute to enable/disable the generation of a depends-on-methods attribute for the <test-method> element. | true |
| generateDependsOnGroups | Enable/disable the generation of a depends-on-groups attribute for the <test-method> element. | true |
In order to configure this reporter you can use the -reporter option in the command line or the Ant task with the nested <reporter> element. For each of these you must specify the class org.testng.reporters.XMLReporter. Please note that you cannot configure the built-in reporter because this one will only use default settings. If you need just the XML report with custom settings you will have to add it manually with one of the two methods and disable the default listeners.
<parameter name="n" value="42" /> <exclude name="broken" /> <class name="test.listeners.ResultEndMillisTest" />
and here is its YAML version:
name: SingleSuite
threadCount: 4
parameters: { n: 42 }
tests:
- name: Regression2
parameters: { count: 10 }
excludedGroups: [ broken ]
classes:
- test.listeners.ResultEndMillisTest
Here is TestNG's own suite file, and its YAML counterpart.
You might find the YAML file format easier to read and to maintain. YAML files are also recognized by the TestNG Eclipse plug-in. You can find more information about YAML and TestNG in this blog post.
Back to my home page. Or check out some of my other projects: